Rationally Inattentive Vision and Planning
This research is motivated by the increasing need for simultaneous perception and action planning in modern information-rich autonomy. Due to the wide availability of low-cost and high-performance sensing devices, obtaining a large amount of sensor data has become easier in many applications. Nevertheless, operating a sensor at its full capacity may not be the best strategy for resource-constrained robots, especially if it drains its scarce power or computational resources with little benefit. As sensor modalities increase, how to achieve a given task with minimum perceptual resources, e.g., with reduced sensing/communication frequencies or sensor gains, becomes increasingly relevant.
In the first phase of this project, we propose a task-dependent attention allocation for vision-based autonomous navigation inspired from attention mechanisms in humans. The proposed mechanism helps the robot to analyze the visual information relevant to the task at hand while neglecting the rest of the available data. In the second phase, we develop a framework to predict and incorporate the perception cost in the motion planning stage, which help the autonomous agent to find motion plans that can be executed with both minimum control and perception efforts. We modify existing motion-planning algorithms (like sampling-based methods) to be able to integrate the perception effort.
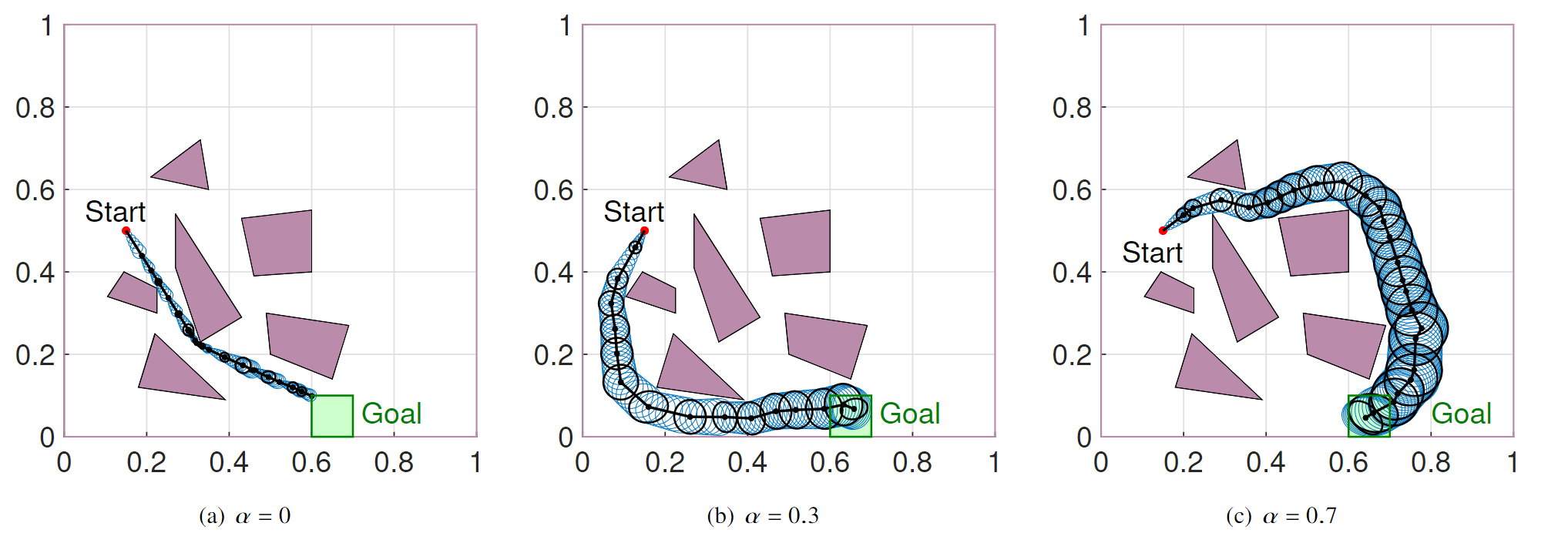
Optimal path plans obtained for different values of perception effort intensity α.
</div>
Related Publications:
A Smoothing Algorithm for Minimum Sensing Path Plans in Gaussian Belief Space AR. Pedram , T. Tanaka, American Control Conference, 2023 [Link]
Gaussian Belief Space Path Planning for Minimum Sensing Navigation, AR. Pedram , R. Funada, T. Tanaka, IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022 [Link]
Dynamic Allocation of Visual Attention for Vision-based Autonomous Navigation under Data Rate Constraints, AR. Pedram, R. Funada, T. Tanaka, IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 2021 [Link]
Rationally Inattentive Path-Planning via RRT*, AR. Pedram, J. Stefan, R. Funada, T. Tanaka, American Control Conference, 2021 [Link]